How To Find Book Value Of Equity
What is Disinterestedness?
In finance, equity is the market place value of the assets owned past shareholders later on all debts have been paid off. In accounting, disinterestedness refers to the book value of stockholders' equity on the balance sheet , which is equal to assets minus liabilities. The term, "disinterestedness", in finance and bookkeeping comes with the concept of fair and equal treatment to all shareholders of a business on a pro-rata basis.
Paradigm: CFI's Intro to Corporate Finance Form
How Equity Works
Owners of a company (whether public or private) have shares that legally represent their buying in the visitor. Each share of the same class has the exact aforementioned rights and privileges every bit all other shares of the same course. This is part of the term's significant – disinterestedness meaning "equal".
Companies tin issue new shares past selling them to investors in exchange for greenbacks. Companies use the gain from the share auction to fund their business concern, grow operations, rent more people, and make acquisitions. Once the shares take been issued, investors can buy and sell them from each other in the secondary marketplace (how stocks ordinarily merchandise on an exchange).
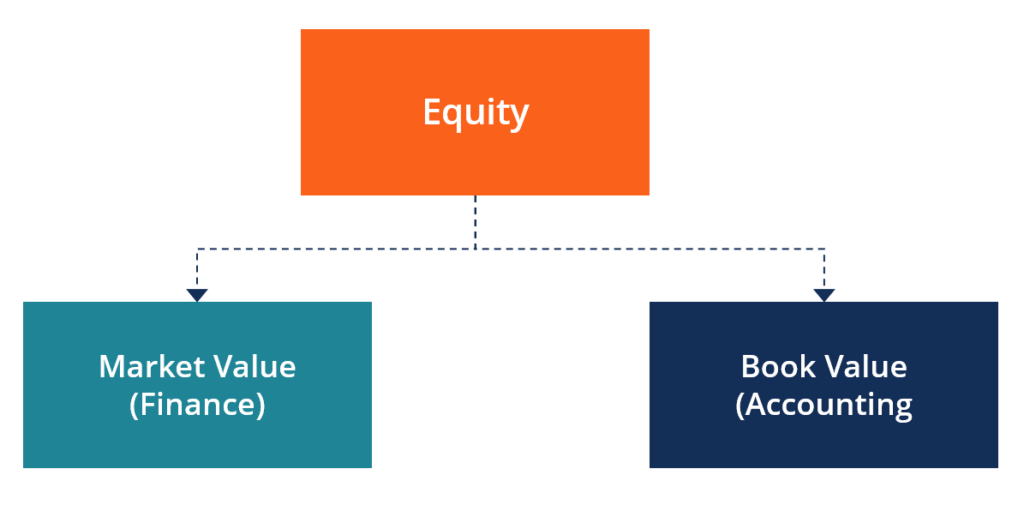
Types of Equity
There are two master applications of the term, each of which is discussed below:
#1 Market Value of Disinterestedness (Finance)
Financial analysts are typically concerned with the market value of disinterestedness, which is the current toll or off-white value they believe shares of the business are worth. Since finance professionals want to know how much of a return they can make on an investment, they need to understand how much the investment will cost them, and how much they believe they can sell information technology for.
Marketplace Value Formula
There are various ways to calculate or estimate the market value of equity for a visitor. Beneath are several methods that tin exist used to calculate the value:
- Market capitalization – equal to the number of shares outstanding x market price (this is merely for public companies)
- Cyberspace Nowadays Value (NPV) of all future equity cash flows of the business
- Comparable Company Analysis
- Precedent Transactions
To learn more than most how fiscal analysts value companies, check out CFI's Business organization Valuation Fundamentals Course.
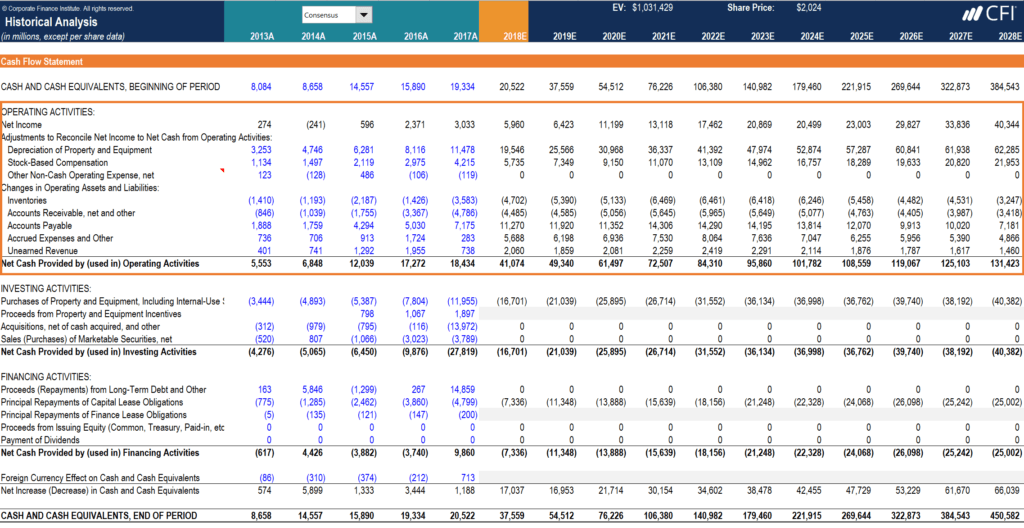
Instance
In the example below from CFI's Fiscal Modeling Course virtually Amazon, you can see how an analyst can build a Discounted Cash Period (DCF) model to forecast the company's cash flows into the future so discount them back to the present. Later on netting out debts owed, the resulting value is divided by the number of shares outstanding to go far at the intrinsic value of equity per share.
#2 Book Value of Equity (Accounting)
Accountants are concerned with recording and reporting the financial position of a company, and, therefore, focus on calculating the book value of disinterestedness. In order for the balance sheet to rest, the formula Disinterestedness = Avails – Liabilities must be truthful.
Book Value Formula
There are various means to calculate or calculate the book value of disinterestedness for a company. Below are several methods that can exist used to calculate the value:
- Assets – Liabilities
- Share Capital + Retained Earnings
- Share Capital + Contributed Surplus + Cumulative Net Earnings – Cumulative Dividends
To learn more nigh fiscal statements, bank check out CFI's Bookkeeping Courses .
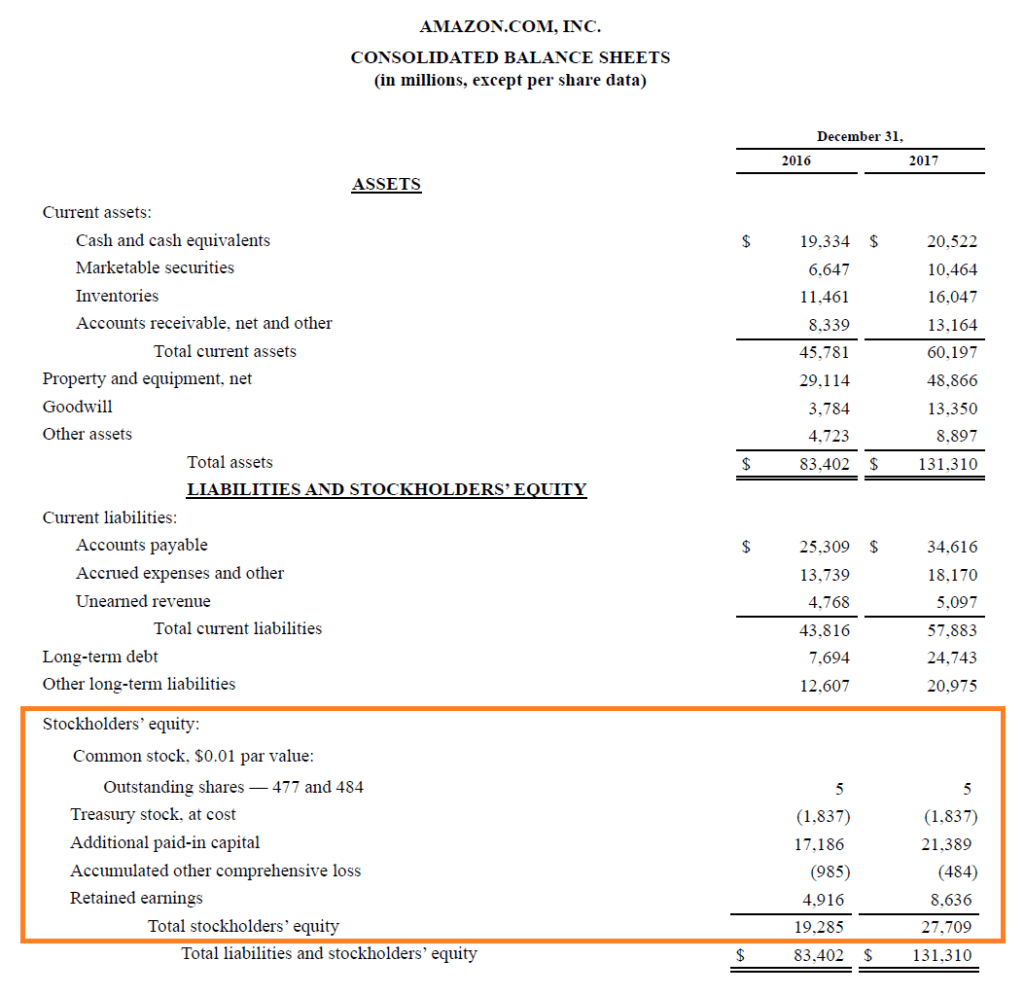
Example
Below is a screenshot of Amazon's 2017 balance sheet, which shows a breakdown of the book value of its stockholders' equity . Equally you can see, in 2017, the company reported full stockholders' disinterestedness of $27.7 billion.
Marketplace Value vs. Volume Value (Future vs. Past)
The main departure between market value and book value is that market value is forrad-looking (expectations about the future), and book value is backward-looking (recording a history of what happened in the past).
Finance professionals are typically concerned with forecasting or estimating how a visitor will perform in the future. Accountants, on the other manus, are focused on providing a detailed and accurate pic of what has really happened, and, thus, they focus on the past.
Toll/Volume Ratio
Since one is forwards-looking and the other is backward-looking, there may exist a large discrepancy between market value and book value. This is not necessarily a "adept" or "bad" thing.
In order to assess how large the gap is between the market value and book value of a visitor'southward equity, analysts will often utilise the Cost-to-Book (P/B) ratio .
Additional Resource
CFI offers the Fiscal Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™ certification program for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful:
- Common Stock
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Guide
- Dividend Per Share (DPS)
- Preferred Shares
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/equity-definition/
Posted by: thomashiplent.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find Book Value Of Equity"
Post a Comment